Force - Weekly Blog (12/14-12/18)
 |
| Balanced and Unbalanced Forces by The Physics Classroom |
Summary
Force is the push or pull on an object. But what happens if more than one force acts on an object? The combination of two or more forces at once is called the net force. When two forces are acting in the same direction, the net force is the sum of all of the forces, and the object will move in the direction the forces are pushing. If two forces of different rates are acting in opposite directions, the net force is the difference between the two forces. The object moves in the direction the larger force. If two forces of the same rate act in opposite directions, the net force is zero, and the object will not move.
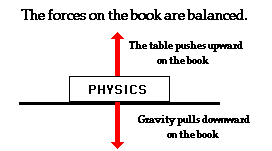
We can show the forces acting on an object with force diagrams. The arrows show the direction and size of the force on an object. A force is considered balanced if there are two forces acting on one object that are the same size, but are facing in opposite directions. In balanced forces, objects that are not moving stay still, and objects that are moving continue at the same speed and direction. A force is called an unbalanced force when two forces on an object are not equal in size, they are called unbalanced forces. In unbalanced forces, if an object is not moving, it will start to move, and objects that are moving will change speed or direction.
An example of a balanced force would be the forces acting on you when you are walking. When you are walking, the forces that are pushing on you are the gravitational pull, which is pulling you down, and the push upwards from the surface of the Earth. This is a balanced force because both forces are equal in size, but are facing opposite directions. If the force became unbalanced, you may start to float, because the gravitational pull would not be pulling you back towards the Earth. You may also sink to the floor if the upward push of the Earth is unbalanced.
A cross-cutting concept that I noticed this week is Cause and Effect. The cause is that the force on an object leads to the object moving at a specific speed. For example, if you kick a soccer ball, the ball will move depending on the direction and force that you kicked it with. This relationship can be tested by applying various amounts of force and comparing the direction and speed that it causes the object to move in. Understanding this cause and effect relationship has helped me learn more about force and how it can affect the direction and force at which an object will move.
SP3: Developing And Using Models
This week, we used force models to represent the forces acting on an object. With models, we were able to compare multiple forces on an object to see which direction the object is moving in. We used models to explain and predict the direction and strength of forces to learn more about how they can affect. Learning about models has helped me learn a lot more and how various forces can affect the direction and speed in which an object will move.XCC: Cause and Effect
A cross-cutting concept that I noticed this week is Cause and Effect. The cause is that the force on an object leads to the object moving at a specific speed. For example, if you kick a soccer ball, the ball will move depending on the direction and force that you kicked it with. This relationship can be tested by applying various amounts of force and comparing the direction and speed that it causes the object to move in. Understanding this cause and effect relationship has helped me learn more about force and how it can affect the direction and force at which an object will move.
Comments
Post a Comment