Evolution - Weekly Blog (10/8-10/12)
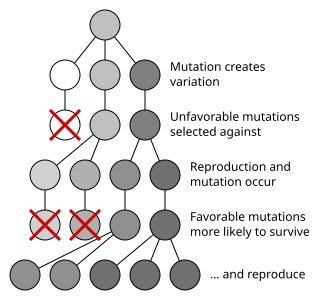 |
| File: Mutation and selection diagram by Elembis |
Summary
Evolution is a change in the hereditable traits within a population, over generations. There are five mechanisms for evolution. The mechanisms include genetic drift, mating with specific traits, mutations, movement or gene flow, and adaptation or natural selection.
Genetic drift is a slow change of specific genes in a population. There are two effects that can cause genetic drift, called the founder effect and bottlenecking. The founder effect is when a small sample with a specific trait moves to a different place and only procreates within itself. The next effect is bottlenecking, which is when a disaster wipes out most of a population. Only the surviving traits can be passed on. A mutation is a change in the DNA. Mutations are always random and can be defined as an error in the DNA code. Some mutations can have a small effect and do not matter to evolution. However, some mutations, such as long ears in cats, can affect all of the future generations. The next generation of cats may have longer ears as well because of the DNA mutation.
The next mechanism of evolution is gene flow or migration. Gene flow is a movement in the genes that happens from one population to another. If a trait has been passed from one population to another, that trait can affect the future generations. The final mechanism is natural selection, which is one of the most basic mechanisms of evolution. Natural selection can be caused by variation in the traits, differential reproduction, or heredity, which affect the traits of the future generations.
SP4: Analyzing and Interpreting Data
This week, we analyzed and interpreted the data that we obtained in our experiment. By analyzing the data into a graph, it was easier to see the change in the variable (trait) and how that affected the whole population. Analyzing the data and sorting it made it a lot easier to interpret the data and answer questions about what we obtained in the experiment. By analyzing and interpreting the data, it was a lot easier to understand what evolution is and how a small change in the trait can affect future generations.
XCC: Cause and Effect
This week, I observed a cause and effect relationship between the traits passed on in a gene, and how evolution affects the future generations. In this cause and effect relationship, the cause is the variation in traits that are passed on to the future generation. This causes the effect that the next generation may pass on that trait, over time, causing evolution. This cause and effect relationship has helped me understand more about evolution and how it can affect the future generation.
Comments
Post a Comment